Diabetic Retinopathy in Pakistan | Cost of Laser Treatment
- Home
- Services
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the complications of diabetes mellitus. It affects the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Retinopathy occurs when diabetes damages the tiny blood vessels in the retina. This damage can lead to problems with your vision, including blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness due to diabetes mellitus.
Do all Diabetic Patients have Retinopathy?
It is an ocular manifestation of systemic disease that affects up to 80% of all patients who have had diabetes for 10 years or more.
As long as a patient has diabetes, there is a chance for retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent vision loss. Careful control of your blood sugar level, blood pressure, and cholesterol will help delay and possibly prevent vision loss.
At first, diabetic retinopathy may cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems. The abnormal growth of new blood vessels in the retina can lead to serious vision problems such as vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment, or glaucoma. Eventually, however, diabetic retinopathy can result in blindness.
Smoking
Often there are no symptoms in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy begins before a patient has any symptoms. As the problem gets worse blurred vision and floaters are seen.
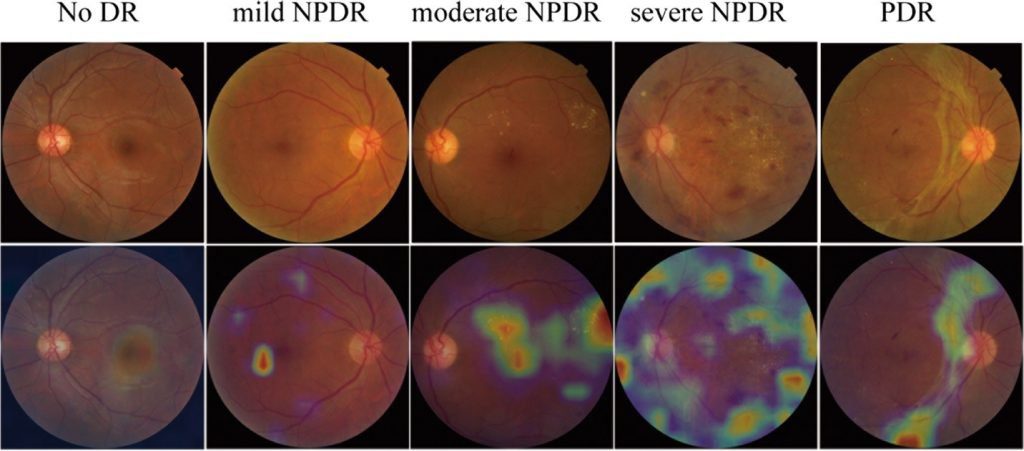
Early diabetic retinopathy. Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) is the most common type of diabetic retinopathy. It can be described as mild, moderate or severe. When you have NPDR, the walls of the blood vessels in your retina weaken. Tiny bulges protrude from the vessel walls, sometimes leaking fluid and blood into the retina. These bulges are called microaneurysms. As the condition progresses, the smaller vessels may close entirely and the larger retinal veins may begin to dilate and become irregular in diameter. Nerve fibers in the retina may begin to swell. Sometimes the central part of the retina (macula) begins to swell, too. This is known as macular edema.
Advanced diabetic retinopathy. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) is the most severe type of diabetic retinopathy. When you have PDR, abnormal blood vessels grow in the retina. Sometimes the new blood vessels grow or leak into the clear, jelly-like substance that fills the center of your eye (vitreous). Eventually, scar tissue stimulated by the growth of new blood vessels may cause the retina to detach from the back of your eye. If the new blood vessels interfere with the normal flow of fluid out of the eye, pressure may build up in the eyeball. This can damage the nerve that carries images from your eye to your brain (optic nerve). Diabetic retinopathy can happen to anyone who has diabetes. The risk of diabetic retinopathy is highest if the patient has
- Poor diabetic control
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
Diabetic retinopathy is best diagnosed with a dilated eye exam. During the exam, the doctor looks for:
- Abnormal blood vessels
- Swelling, blood or fatty deposits in the retina
- Damage to the nerve tissue
- Growth of new blood vessels and scar tissue
- Bleeding in the center of the eye
How is Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosed?
To diagnose diabetic retinopathy a detailed examination by an experienced ophthalmologist is needed. Your eye doctor also may request an optical coherence tomography (OCT) exam. This imaging test provides cross-sectional images of the retina that show the thickness of the retina and whether fluid has leaked into retinal tissue. Later, OCT exams can be used to monitor treatment effectiveness.
What is the Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Prevention is the best treatment for diabetic retinopathy. The strict control of blood sugar will significantly reduce the long-term risk of vision loss.
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the type of diabetic retinopathy you have, its severity, and how well it may respond to specific treatments.
The first option for diabetic macular edema treatment is the intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF or steroids.
If abnormal blood vessels have grown on the retina (proliferative diabetic retinopathy), laser surgery can be effective in shrinking those vessels and preventing them from growing in the future. Multiple laser treatments over time are sometimes necessary. Laser surgery does not cure diabetic retinopathy and does not always prevent further loss of vision.
If there is advanced damage to the eye because of retinopathy, a microsurgery called a vitrectomy may help.
We at visionX provide you with ultimate advanced treatment options. We are equipped with the most advanced Operation theatre, OCT machine, and competent eye surgeons that can offer you the best treatment options regarding your vision.
VisionX Laser and Eye Clinic are comprised of the best eye doctors in Lahore. We have vast experience in diagnosing and treatment of routine and rare eye diseases. We have the best eye surgeon in Lahore and the best eye surgeons that are skilled enough for ensuring the best visual and surgical results.
We claim the best eye center in Lahore and one of the state of the art best eye hospital in Lahore that is equipped with the latest machinery and great ambiance. VisionX Laser and Eye Clinic comprise all diagnostic services and Lasers and you can get all eye-related services under one roof at very affordable prices.
If you are near Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research Centre or live nearby you can easily locate us by searching best eye surgeon near me or the best eye center in Lahore.
